Global Economy: Forecasts and Challenges
In October 2024, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) published its report, World Economic Outlook, noting that despite uneven growth, the global economy demonstrates resilience accompanied by a gradual decline in inflation.
Economic Growth Forecasts
The IMF projects moderate global economic growth in the coming years:
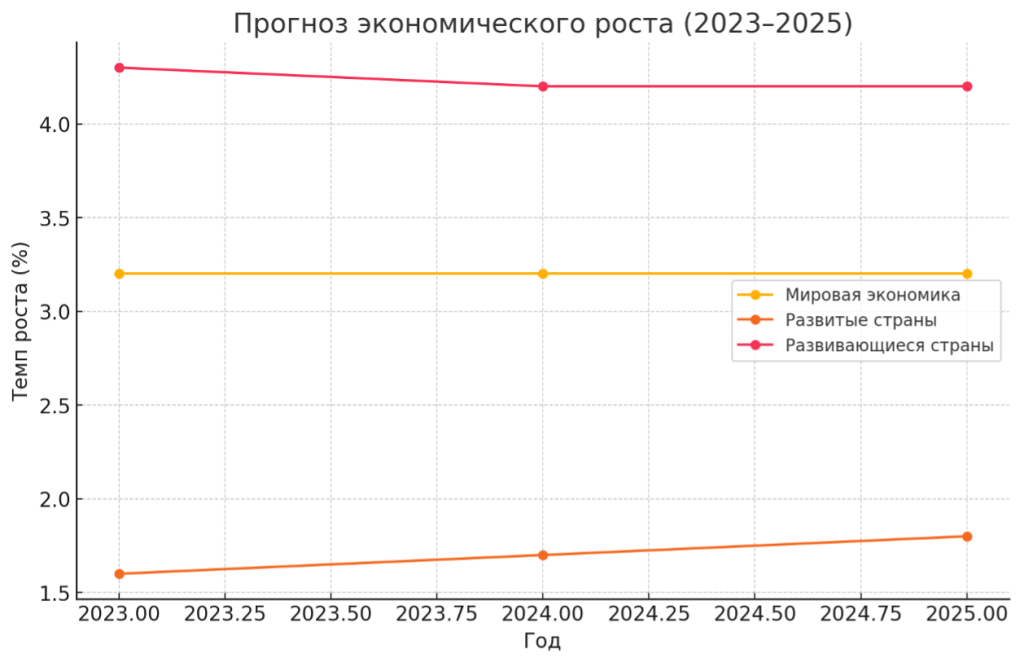
- Global level: The global economy is expected to grow by around 3.2% in 2024 and 2025, consistent with the 2023 figure. However, this level is below the historical average of 3.8% recorded from 2000 to 2019.
- Advanced economies: A slight increase is forecasted, from 1.6% in 2023 to 1.7% in 2024 and 1.8% in 2025.
- Emerging markets and developing economies: A slight slowdown is expected, with growth decreasing from 4.3% in 2023 to 4.2% in 2024 and 2025.
The graph below illustrates the growth forecast for the three economic categories:
Inflation Trends
One of the key achievements of the global economy has been the reduction in inflation. IMF projections indicate a gradual decline:
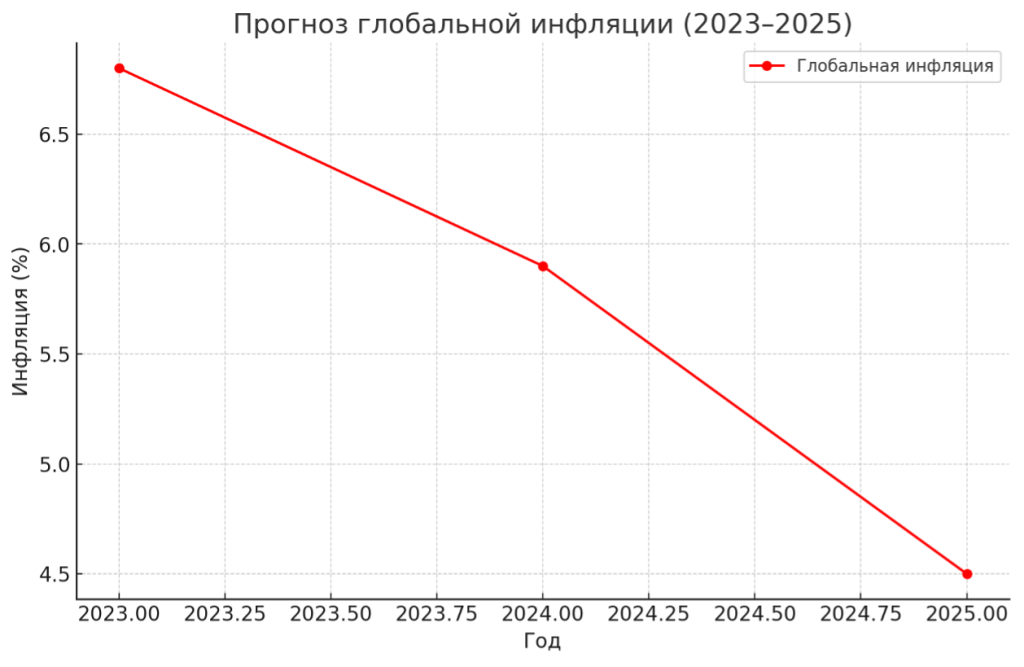
- Global inflation: It is decreasing from 6.8% in 2023 to 5.9% in 2024 and is forecasted to reach 4.5% in 2025.
- Advanced economies: A faster return to target inflation levels is anticipated compared to emerging markets and developing economies.
The graph below illustrates the inflation reduction trend:
Factors Affecting Economic Resilience
- Monetary policy: Central banks have significantly raised interest rates to restore price stability. However, changes in housing and mortgage markets have mitigated the short-term impacts of these measures.
- Structural rigidities: Persistent structural issues hinder the efficient allocation of capital and labor to productive companies, which restrains productivity growth.
- Geoeconomic fragmentation: Slowing growth in major emerging markets, such as China, negatively affects their trading partners, emphasizing the importance of multilateral cooperation.
IMF Recommendations
- Monetary policy: Ensure a smooth decline in inflation while avoiding abrupt changes that could destabilize the economy.
- Fiscal consolidation: Restore fiscal space for maneuvering and prioritize investments while ensuring debt sustainability.
- Structural reforms: Stimulate supply through reforms aimed at boosting productivity and accelerating the transition to green energy.
